Sustainable Branded Gifts A Guide
Sustainable branded gifts set the stage for a thoughtful approach to gift-giving, exploring environmentally conscious and socially responsible options. This guide delves into the various aspects of creating and promoting such gifts, from material selection to marketing strategies.
The discussion encompasses defining sustainable gifts, understanding the target audience, and considering design, production, and marketing strategies. Key considerations include ethical sourcing, innovative design, and effective communication to resonate with consumers seeking environmentally friendly and socially responsible choices.
Defining Sustainable Branded Gifts
Sustainable branded gifts represent a conscious shift in the gifting industry, prioritizing environmental and social responsibility. These gifts are carefully crafted from ethically sourced materials and produced using eco-friendly methods. They’re designed to minimize negative impacts on the planet and promote fair labor practices, differentiating them significantly from traditional gifts.
These gifts are not just about using recycled materials; they encompass a broader ethos of mindful consumption. They aim to reduce waste, support sustainable communities, and promote responsible production. This conscious approach resonates with consumers increasingly seeking products with a positive environmental and social footprint.
Sustainable Material Characteristics
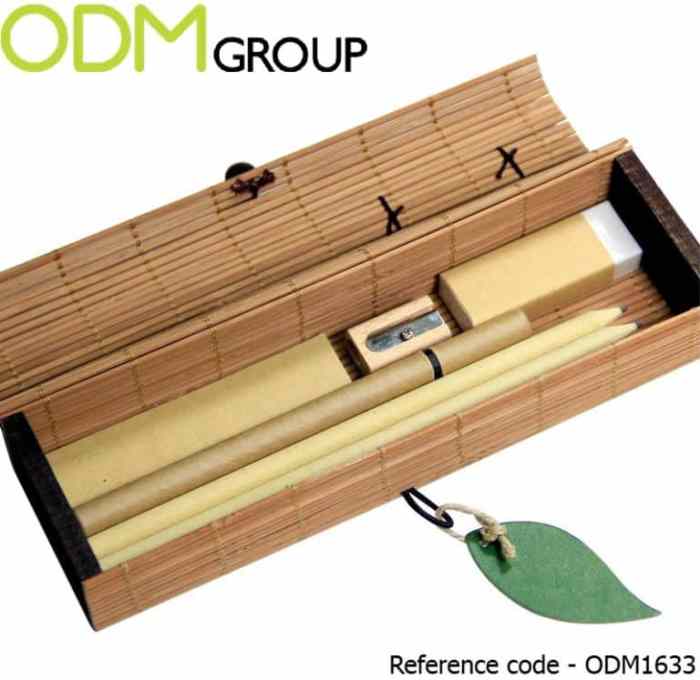
Sustainable gifts are distinguished by the choice of materials and the methods used to create them. These gifts prioritize renewable resources and recycled materials. They are designed to minimize waste and resource depletion, unlike conventionally produced items that often rely on finite resources and contribute to pollution. Furthermore, they often involve locally sourced materials, reducing transportation emissions and supporting regional economies.
Comparison of Sustainable Materials
The table below highlights key differences between various sustainable materials used in gift creation. The selection of materials directly influences the environmental impact of the final product.
| Material | Source | Environmental Impact (General) | Social Impact (General) | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bamboo | Fast-growing, renewable plant | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | Sustainable farming practices can support local communities | Bamboo pens, phone cases, decorative items |
| Recycled Plastic | Post-consumer plastic waste | Reduces reliance on virgin plastic, lowers landfill burden | Creates jobs in recycling and manufacturing industries | Bags, water bottles, desk organizers |
| Organic Cotton | Grown without harmful pesticides and fertilizers | Reduced chemical pollution, healthier soil | Fair wages and safe working conditions for farmers | T-shirts, tote bags, notebooks |
| Cork | Cork oak trees (sustainable harvesting) | Renewable resource, naturally water-resistant | Supports sustainable forestry practices | Bottle stoppers, coasters, gift tags |
Environmental and Social Benefits
Sustainable branded gifts offer a variety of environmental and social advantages. By opting for sustainable choices, consumers contribute to a healthier planet. The shift toward sustainable materials and production methods reduces the reliance on finite resources, lowering our collective environmental footprint. Furthermore, sustainable practices often support fair labor practices, contributing to better working conditions and economic empowerment for producers.
“Choosing sustainable gifts fosters a more responsible and ethical consumer culture, leading to a healthier environment and stronger communities.”
Target Audience and Market Trends

Source: ecolifewise.com
Sustainable branded gifts are increasingly sought after by a discerning consumer base. This segment is not just environmentally conscious; they are often actively seeking products that align with their values and lifestyles. Understanding the motivations and preferences of this target audience is crucial for businesses looking to tap into this growing market. Identifying trends and regional variations in demand allows for tailored marketing strategies and product development.
Demographics and Psychographics of Sustainable Gift Seekers
Consumers drawn to sustainable branded gifts often fall into specific demographic and psychographic categories. They are typically younger generations, Millennials and Gen Z, with a strong emphasis on ethical consumption and environmental responsibility. These consumers prioritize experiences over material possessions and seek products that reflect their values. They are also highly engaged with social media and are influenced by online reviews and recommendations. Moreover, they tend to have higher disposable incomes and are more willing to pay a premium for sustainable products.
Emerging Trends in the Sustainable Product Market
The market for sustainable products is experiencing a rapid evolution. The trend toward zero-waste and circular economy models is evident, influencing the design and manufacturing of products. Consumers are actively seeking reusable, repairable, and recyclable options. There’s a rising demand for products made from recycled materials or sustainably sourced ingredients. This includes items crafted from organic cotton, bamboo, or recycled plastics. This trend extends beyond just the product itself; the packaging and delivery processes are increasingly being scrutinized for their environmental impact.
Regional and Cultural Variations in Demand
Demand for sustainable gifts varies across regions and cultures. Western countries, particularly those in Europe and North America, have a well-established market for sustainable products, driven by long-standing environmental awareness campaigns. Asia is witnessing a surge in demand, especially in countries like Japan and South Korea, where the emphasis on sustainability is growing. However, the specifics of sustainable practices vary culturally. For instance, some cultures might prioritize local and traditional materials, while others might focus on reducing waste. Understanding these nuances is critical for effectively marketing sustainable gifts to different regions.
Motivators Driving Sustainable Gift Choices
| Motivator | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Consciousness | Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their choices and seek products that minimize harm to the planet. |
| Ethical Sourcing | Consumers prioritize products made with ethical labor practices and sustainable sourcing methods. |
| Social Responsibility | Consumers seek gifts that support positive social impact and contribute to a better world. |
| Personal Values | Gifts reflect the recipient’s values and preferences, aligning with their lifestyle choices. |
| Long-Term Value | Consumers favor products that are durable, reusable, and have a long lifespan. |
Design and Production Considerations

Source: greenpearls.com
Sustainable branded gifts necessitate a careful approach to design and production, ensuring ethical sourcing, minimizing environmental impact, and maximizing longevity. A thoughtful process from initial concept to final delivery is crucial to the brand’s values and resonating with environmentally conscious consumers. The choice of materials, manufacturing methods, and packaging all contribute to the overall sustainability of the product.
Ethical Sourcing and Fair Trade Practices
Ethical sourcing is paramount in sustainable gift production. It ensures fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for human rights throughout the supply chain. Companies should prioritize suppliers committed to ethical labor practices, transparent supply chains, and adherence to fair trade principles. This includes verifying certifications like Fair Trade or B Corp, which guarantee adherence to these standards. By choosing ethically sourced materials, businesses contribute to a more equitable and sustainable global economy.
Innovative Design Approaches for Longevity
Innovative design approaches are essential for creating sustainable branded gifts. Minimizing waste and maximizing longevity are key considerations. Designing for durability, repairability, and upcycling can significantly extend the product’s lifespan. Using recycled or renewable materials, incorporating modular designs that allow for component replacement or upgrades, and promoting creative reuse options all contribute to a circular economy model. For instance, a gift set with interchangeable components, such as a reusable water bottle with a changeable band, allows for future upgrades and minimizes waste.
Packaging Options for Sustainable Gifts
The choice of packaging plays a critical role in the overall environmental footprint of a sustainable gift. Sustainable packaging options include using recycled and biodegradable materials, reducing packaging size and weight, opting for compostable or recyclable packaging, and utilizing minimal packaging. For example, a gift box made from recycled cardboard with a biodegradable liner is a more sustainable option compared to a box made of virgin plastic. Furthermore, choosing packaging that integrates the brand’s message about sustainability strengthens the overall impression.
Eco-Friendly Production Processes
Various eco-friendly production processes are available for sustainable gifts. These processes minimize environmental impact by reducing water and energy consumption, minimizing waste generation, and employing responsible chemical use. Examples include using renewable energy sources in the manufacturing process, adopting water-saving technologies, and using biodegradable inks and adhesives.
| Production Process | Eco-Friendly Method | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Manufacturing | Transition to renewable energy sources, water-efficient machinery, and closed-loop systems | Reduced carbon footprint, minimized water usage, less waste generation |
| 3D Printing | Using recycled materials, optimizing design for minimal material use, and selecting eco-friendly filaments | Reduced material consumption, minimized waste, potential for on-demand production |
| Craft Production | Using locally sourced, recycled, or repurposed materials, minimizing packaging, and employing sustainable handcrafting techniques | Reduced transportation emissions, local job creation, minimal waste generation |
Marketing and Promotion Strategies

Source: umbelorganics.com
Effective marketing strategies for sustainable branded gifts require a nuanced approach, emphasizing transparency and ethical communication. Consumers are increasingly discerning about the environmental and social impact of their purchases, and authenticity is paramount. Highlighting the sustainability features of the gifts, rather than simply stating they are “sustainable,” builds trust and fosters genuine engagement.
Successful marketing campaigns for sustainable gifts must resonate with the target audience’s values and concerns. This requires understanding the motivations behind their choices and tailoring the messaging accordingly. Clear, concise communication about the ethical sourcing, manufacturing processes, and environmental benefits of the gifts is crucial for building a loyal customer base.
Effective Marketing Strategies
Transparency and authenticity are key elements of successful marketing campaigns for sustainable branded gifts. Communicating the entire journey of the product, from raw materials to final packaging, fosters trust and builds a connection with environmentally conscious consumers. This approach positions the brand as a partner in the consumer’s sustainable lifestyle, rather than simply a seller of goods. Furthermore, emphasizing the social responsibility and fair labor practices associated with the products resonates with a growing segment of ethically-minded customers.
Creative Marketing Campaign Examples
Several creative campaigns highlight the sustainability of products. A campaign showcasing the lifecycle of a gift, from the tree to the finished product, can be highly effective. For instance, a company manufacturing gifts from recycled materials could illustrate the process of collecting, processing, and transforming the recycled materials into the final product. Another example is a campaign featuring testimonials from artisans or farmers who participated in the production process, highlighting the positive impact of the gifts on local communities. A third approach is using storytelling to emphasize the journey of a gift.
Showcasing Sustainable Features
The sustainable features of the gifts should be communicated to the target audience. This can be achieved through detailed product descriptions that article the specific materials, manufacturing processes, and certifications related to sustainability. For example, highlighting the use of recycled or reclaimed materials, the fair trade certification, or the reduced carbon footprint of the production process. Visual aids, such as infographics or videos, can be very helpful in making the sustainable features more accessible and engaging for the target audience. Photographs showcasing the artisans or communities involved in creating the gifts can also effectively communicate the social impact of the product.
Social Media Strategies for Sustainable Gifts
Social media plays a vital role in raising awareness about sustainable gifts. Consistent and engaging content is essential for building brand awareness and driving sales. A well-structured social media strategy should incorporate several key elements, such as showcasing the sustainable features of the products, highlighting the ethical practices employed in their creation, and featuring stories from the communities involved in the process. Engagement with the target audience through interactive posts and live Q&As can further solidify the brand’s commitment to sustainability.
| Social Media Platform | Strategy Focus | Example Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Visual storytelling, high-quality images/videos, behind-the-scenes content, influencer collaborations. | Showcase the sustainable materials, feature artisans, and create engaging reels demonstrating the product’s lifecycle. | |
| Building a community, sharing stories, running contests/giveaways, engaging with comments. | Create a Facebook group dedicated to sustainable living, share articles about environmental issues, and run contests to promote sustainable products. | |
| Quick updates, news about sustainable initiatives, engaging in conversations, promoting relevant hashtags. | Tweet about new sustainable products, share inspiring stories about environmental protection, and engage in discussions about sustainability topics. | |
| TikTok | Short-form videos, showcasing the product in action, creating trending challenges, collaborating with influencers. | Create short videos demonstrating the product’s features, run creative challenges related to sustainable living, and collaborate with influencers to promote sustainable gifting. |
Case Studies and Examples

Source: jucycorporategifts.com
Examining successful examples of sustainable practices in branded gifts provides valuable insights for businesses seeking to integrate environmentally conscious strategies. Understanding how other companies have successfully implemented sustainable initiatives can inform decision-making and inspire new approaches. These examples illuminate not only the practical applications of sustainability but also the potential for profitability and brand enhancement.
A key aspect of sustainable branded gifts is the alignment of environmentally friendly practices with the overall brand message. Successful companies often weave sustainability into their core values, creating a strong connection with environmentally conscious consumers. This alignment not only resonates with target audiences but also fosters a positive brand image, increasing consumer trust and loyalty.
Successful Companies and Their Strategies
Several companies have demonstrated a commitment to sustainability in their branded gift offerings. Their approaches offer diverse examples of successful strategies.
- Patagonia: Patagonia’s dedication to sustainability extends to its branded merchandise. Their commitment to using recycled and organic materials in their products is well-documented, showcasing a holistic approach to environmental responsibility. Patagonia’s brand image is deeply rooted in environmentalism, and its branded gifts reinforce this core message. Their approach highlights the potential of aligning a brand’s identity with sustainable practices.
- Uncommon Goods: Uncommon Goods often features eco-friendly gifts and products. They emphasize the origin and materials of the items, highlighting the sustainable practices of their producers. They create a transparent approach to sustainability, fostering trust with consumers. Their selection of products and emphasis on provenance encourages customers to consider the environmental impact of their purchases.
- Warby Parker: Warby Parker’s business model demonstrates how a company can achieve sustainability across its supply chain, including its branded gifts. Their use of recycled and sustainably sourced materials in their packaging and gifts demonstrates their commitment to reducing waste and conserving resources. They emphasize the lifecycle of the product and its materials, making it transparent for consumers.
Comparing and Contrasting Sustainability Initiatives
A comparison of different sustainability initiatives reveals various approaches and levels of success. Some companies focus on reducing waste in their packaging, while others prioritize the use of recycled or renewable materials. The effectiveness of a strategy depends on its alignment with the brand’s values and its resonance with the target audience. Factors like cost, consumer perception, and brand image all play a significant role in the success of sustainable initiatives.
Key Success Factors for Sustainable Branded Gifts
The table below highlights key success factors for companies implementing sustainable practices in their branded gifts. These factors underscore the importance of strategic planning and consumer awareness.
| Success Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Selection | Choosing eco-friendly materials like recycled plastics, organic cotton, or sustainably sourced wood directly influences the environmental impact of the gift. |
| Packaging Optimization | Minimizing packaging materials and utilizing recycled or biodegradable options reduces waste and improves the gift’s environmental footprint. |
| Supply Chain Transparency | Communicating the origin and production methods of the materials builds trust and demonstrates a commitment to ethical sourcing. |
| Consumer Engagement | Promoting sustainability through marketing and communication strategies resonates with environmentally conscious consumers and builds brand loyalty. |
| Financial Viability | Sustainable practices can be integrated without compromising profitability, showcasing that environmental responsibility can be profitable. |
Measuring Sustainability Impact
Evaluating the environmental and social footprints of sustainable branded gifts is crucial for transparency and accountability. Accurate measurement allows businesses to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and consumers to make informed choices. This process involves a multifaceted approach, considering factors beyond the gift itself, encompassing the entire lifecycle.
Environmental Impact Assessment Methods
Understanding the environmental impact requires a systematic evaluation of the materials, manufacturing processes, and transportation involved in producing and delivering the gifts. Life cycle assessment (LCA) is a valuable tool for quantifying the environmental effects across the entire product’s lifecycle. This involves analyzing energy consumption, water usage, waste generation, and greenhouse gas emissions at each stage. LCA methodologies allow for a comprehensive comparison of different materials and production processes, helping to identify the most sustainable options. For example, a company could use LCA to compare the environmental impact of using recycled plastic versus virgin plastic in a gift box.
Social Impact of Ethical Production Practices
Assessing the social impact of ethical production practices focuses on the well-being of workers throughout the supply chain. Fair labor practices, including fair wages, safe working conditions, and freedom from exploitation, are essential. Companies can implement monitoring systems to track labor conditions and ensure compliance with ethical standards. For instance, certifications like Fairtrade or WRAP can provide a framework for evaluating labor practices. Social audits and worker surveys can also be employed to gather direct insights from those involved in the manufacturing process.
Metrics for Overall Sustainability Evaluation
Several metrics can help assess the overall sustainability of a branded gift. Carbon footprint calculations are a crucial indicator of environmental impact. Social responsibility scores, based on criteria like fair labor practices and community engagement, reflect the social sustainability aspects. Material sourcing, such as the percentage of recycled or sustainably sourced materials used, provides a tangible measure of environmental responsibility. A weighted average of these metrics, along with others like water usage and waste generation, can provide a holistic sustainability score. For example, a gift made from recycled materials, produced in a factory with fair labor standards, and shipped using a sustainable carrier would receive a higher sustainability score compared to a gift made from non-recycled materials and shipped with high carbon emissions.
Sustainability Certifications and Standards, Sustainable Branded Gifts
Various certifications and standards exist to ensure the sustainability of branded gifts. These provide benchmarks and guidelines for companies to meet. A comprehensive understanding of these standards helps identify and implement best practices.
| Certification/Standard | Focus Area | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fairtrade | Fair labor practices, environmental protection | Ensures fair prices for farmers and workers, promotes sustainable agriculture. |
| WRAP (Worldwide Responsible Accredited Production) | Social and environmental compliance | Audits and certifies factories to ensure adherence to ethical and environmental standards. |
| GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) | Organic textiles | Ensures organic production of textiles, promoting environmentally sound practices. |
| FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) | Sustainable forestry | Certifies wood and paper products from responsibly managed forests. |
| B Corp Certification | Social and environmental performance | Evaluates companies’ positive impact on society and the environment. |
Future Trends and Innovations
The market for sustainable branded gifts is rapidly evolving, driven by consumer demand for environmentally conscious products and innovative technologies. This evolution is likely to see a greater emphasis on circularity, transparency, and the integration of technology into the entire product lifecycle, from design and sourcing to disposal.
The next wave of sustainable branded gifts will likely feature a greater emphasis on functionality and longevity, moving beyond simple promotional items to more useful and reusable products. This trend is driven by consumers seeking value and reducing waste. Design will increasingly prioritize durability and repairability, alongside eco-friendly materials.
Potential Future Trends
The future of sustainable branded gifts will be shaped by several key trends. These include a growing preference for gifts with a clear social or environmental impact beyond simple branding. Consumers are increasingly drawn to products with a story, showcasing ethical sourcing and production processes. Furthermore, the focus on circularity will be amplified, with a greater emphasis on reusable and repairable products.
-
- Increased focus on circularity and reuse:
This means designing products for multiple uses, emphasizing repairability, and enabling easy disassembly for material recovery. Consider a reusable water bottle with a customizable, removable label, allowing for a new label each year rather than a new bottle.
-
- Emphasis on transparency and traceability:
Consumers are demanding greater transparency in the supply chains of the products they purchase. This includes detailed information about materials, production processes, and environmental impact. Blockchain technology can play a significant role in providing verifiable and auditable information throughout the supply chain.
-
- Integration of technology for personalized experiences:
Technology can enhance the experience of receiving and using a sustainable branded gift. This might include smart packaging that reveals information about the product’s origin or a digital platform that tracks the product’s journey and provides opportunities for interaction.
Innovative Technologies and Materials
Innovative materials and technologies are revolutionizing the production of sustainable branded gifts.
-
- Bio-based and recycled materials:
Materials like mycelium, bamboo, and recycled plastics are becoming increasingly common in sustainable gift design. Mycelium, a fungal material, can be molded into intricate shapes and is incredibly lightweight.
-
- 3D printing and additive manufacturing:
3D printing allows for the creation of customized and intricate designs using recycled or bio-based materials, reducing waste associated with traditional manufacturing processes. Imagine a custom-designed keychain crafted from recycled plastic filament.
-
- Advanced packaging solutions:
Biodegradable and compostable packaging options are becoming more readily available, minimizing the environmental impact of gift delivery. Using mushroom-based packaging, for example, would be a sustainable and visually appealing option.
Technology’s Role in Transparency and Traceability
Technology is crucial in promoting transparency and traceability in sustainable gift production.
-
- Blockchain technology:
Blockchain can track the journey of a product from raw material to finished good, ensuring ethical sourcing and environmental compliance. This allows consumers to verify the sustainability claims of a gift.
-
- Digital platforms:
Digital platforms can provide detailed information about a product’s origin, manufacturing process, and environmental impact, enhancing transparency for consumers. A QR code on the gift itself could link to a digital platform.
-
- RFID tagging:
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags can track products throughout their life cycle, enabling real-time monitoring and facilitating data collection about their usage and eventual recycling.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
The transition to sustainable branded gifts presents both challenges and opportunities.
| Challenge | Opportunity |
|---|---|
| High initial costs of sustainable materials and technologies | Potential for cost reductions through economies of scale and innovation |
| Lack of consumer awareness about sustainable options | Increased marketing and education efforts to promote awareness and demand |
| Supply chain complexities in sourcing sustainable materials | Collaboration with ethical and sustainable suppliers to build robust supply chains |
Epilogue: Sustainable Branded Gifts
In conclusion, sustainable branded gifts represent a significant shift in the gift-giving industry, highlighting the importance of environmental and social responsibility. The exploration of various materials, production methods, and marketing strategies demonstrates the potential for creating impactful and memorable gifts that align with modern consumer values. This comprehensive guide provides a framework for businesses and individuals to navigate this evolving market and contribute to a more sustainable future through their gift choices.