CIAM Architecture A Comprehensive Overview
CIAM architecture, a crucial component in modern identity and access management, empowers organizations to provide seamless and personalized user experiences. It encompasses a range of technologies and strategies designed to manage user identities, enabling secure and streamlined access to resources. This approach is particularly relevant in today’s digital landscape, where user expectations are high and security is paramount.
The core components of a CIAM system work in concert to create a robust and user-friendly experience. This includes authentication mechanisms, authorization policies, and data management protocols. Different implementation strategies, from cloud-based to on-premises solutions, cater to various organizational needs and resources. This introduction will delve into the key components, implementation strategies, and security considerations of CIAM, providing a holistic view of this critical technology.
Introduction to CIAM Architecture
CIAM, or Customer Identity and Access Management, is a comprehensive approach to managing customer identities and access rights within a digital ecosystem. It goes beyond traditional IAM by focusing on the customer experience, allowing for seamless and personalized interactions. This modern framework provides a centralized platform for managing customer identities across various touchpoints, from registration and authentication to personalized service delivery.
CIAM architecture is crucial for modern businesses to provide a positive and frictionless experience for their customers. By integrating identity management with customer-centric services, CIAM fosters stronger customer relationships and drives loyalty. It’s a critical component for organizations aiming to thrive in today’s digital marketplace.
Core Components of a Typical CIAM Architecture
A typical CIAM architecture comprises several key components working in concert. These include a customer data platform (CDP) for collecting and managing customer data, an identity and access management (IAM) system for controlling user access, and a customer experience management (CXM) system to streamline customer interactions. These components work together to provide a complete customer journey. The interplay of these components is crucial to maintaining a consistent and secure customer experience across various channels.
Types of CIAM Implementations
CIAM implementations can vary based on organizational needs and resources. One common implementation is cloud-based CIAM, which leverages cloud-computing services for scalability and flexibility. This model is often favoured by businesses with dynamic needs or limited IT resources. On-premises CIAM, on the other hand, allows for greater control and customization, often preferred by organizations requiring high security or specific regulatory compliance. Hybrid implementations are also possible, combining aspects of both cloud and on-premises solutions.
Evolution of CIAM Architecture
CIAM architecture has evolved significantly over time. Early IAM systems focused primarily on security, with limited consideration for the customer experience. As digital interactions increased, the need for a more customer-centric approach emerged. This evolution is driven by a desire for enhanced personalization, improved security, and increased efficiency in customer management. The shift towards CIAM reflects the growing importance of customer experience in the digital age.
Key Benefits of Employing CIAM Architecture
The benefits of implementing a CIAM architecture are substantial. These include improved customer satisfaction through personalized experiences, enhanced security by centralizing user data, and streamlined operations by automating key processes. Increased efficiency in customer onboarding and support is also a major advantage, resulting in reduced costs and improved operational effectiveness. Moreover, CIAM fosters a more unified customer view, leading to better decision-making and targeted marketing campaigns.
Comparison of CIAM with Other IAM Approaches
| Feature | CIAM | Other IAM |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Customer experience and personalization | Security and access control |
| Data Management | Comprehensive customer data integration | Limited data integration, often siloed |
| Customer Experience | Seamless and personalized interactions | Focus on security, potentially impacting user experience |
| Scalability | Highly scalable to accommodate growing user bases | Scalability can be limited depending on the implementation |
| Integration | Integrates with various customer touchpoints | Integration is often limited to core systems |
This table highlights the key differences between CIAM and traditional IAM approaches, demonstrating how CIAM prioritizes the customer journey. Other IAM approaches often focus more on security and access control, which can sometimes hinder a positive customer experience.
Key Components and Their Interrelation: Ciam Architecture
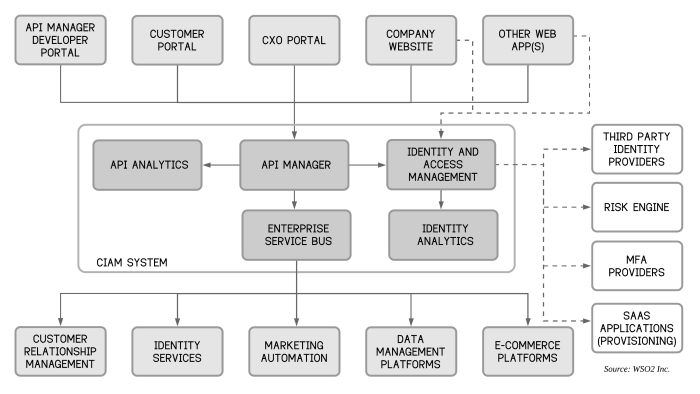
Source: github.io
CIAM architecture, at its core, orchestrates a seamless customer journey by integrating various components. These components work in concert to gather, manage, and leverage customer data to personalize experiences and drive business value. Understanding the intricate interplay between these components is crucial for optimizing the CIAM system’s performance and efficacy.
Functions of Key Components
The CIAM architecture comprises several key components, each with distinct functionalities. These components work collaboratively to provide a comprehensive view of the customer, enabling personalized interactions and targeted marketing campaigns. The primary components include customer data platforms (CDPs), identity and access management (IAM) systems, and marketing automation platforms. CDPs consolidate and analyze customer data, while IAM systems ensure secure access and manage user identities. Marketing automation platforms leverage this data to deliver personalized marketing communications and interactions.
Interaction Between Components
The effective functioning of a CIAM system hinges on the smooth interaction between its various components. A customer’s interaction with one component triggers data exchange and processing within the system. For example, when a customer registers on a website, the registration data is passed to the CDP for storage and analysis. This data is then used by the IAM system to manage the customer’s account and access rights. The CDP’s insights can also be used by the marketing automation platform to personalize marketing communications. This collaborative interaction is essential for delivering a personalized customer experience.
Data Flows Within a CIAM Architecture
Data flows are critical for the success of a CIAM system. Understanding these flows allows for efficient data management and utilization. Data flows originate from various sources, such as websites, mobile apps, and social media platforms. These sources feed data into the CDP, where it is aggregated, cleansed, and enriched. The CDP shares this data with the IAM system for user authentication and authorization. Finally, the data is used by the marketing automation platform to personalize communications and interactions.
Diagram of User Data Flow
The diagram below illustrates the flow of user data through a typical CIAM system. Data from various touchpoints (e.g., website registration, app usage) is collected and transmitted to the CDP. The CDP processes and enriches this data, making it readily available to other components of the CIAM architecture, including the IAM system for identity management and the marketing automation platform for targeted campaigns. The flow is cyclical, as feedback loops enable continuous improvement and optimization.
(Imagine a diagram here. The diagram would show a user interacting with multiple touchpoints, such as a website and an app. Arrows would connect these touchpoints to a CDP. Further arrows would connect the CDP to the IAM system and the marketing automation platform. Feedback loops would be shown connecting the platforms back to the CDP.)
Interfaces and Integrations
The CIAM system must integrate with other business systems to achieve a holistic view of the customer. The following table shows some common interfaces and integrations supported by CIAM.
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems | Integration with CRM systems allows for seamless data exchange and a unified customer view. |
| E-commerce Platforms | Integration with e-commerce platforms enables personalized recommendations and targeted promotions. |
| Marketing Automation Platforms | Integration with marketing automation platforms allows for personalized communications and targeted campaigns. |
| Social Media Platforms | Integration with social media platforms allows for the collection of social data and enhanced customer profiles. |
Use Cases and Implementation Strategies
CIAM implementations are transforming how organizations manage customer identities and access, leading to improved security, enhanced user experiences, and streamlined business processes. This section explores real-world applications, implementation strategies, and key considerations for successful CIAM deployments.
The strategic deployment of CIAM involves a careful consideration of various factors, including the specific needs of the organization, the chosen technology stack, and the desired level of user experience. By understanding the intricacies of implementation and the challenges inherent in these projects, organizations can better prepare for successful integration.
Real-World CIAM Implementations
CIAM solutions are proving valuable across diverse industries. Financial institutions leverage CIAM to streamline account opening and management, providing secure and convenient online banking experiences. Retailers utilize CIAM to personalize customer journeys, offering targeted promotions and recommendations based on individual preferences. E-commerce platforms employ CIAM to improve security and manage customer data, thereby fostering trust and loyalty.
Implementation Strategies
Several approaches are employed for deploying CIAM in diverse environments. One strategy focuses on phased rollouts, starting with a pilot program in a specific department or segment before expanding to the entire organization. Another approach emphasizes integration with existing systems, minimizing disruption, and maximizing compatibility. Furthermore, a strategy may prioritize cloud-based solutions for scalability and cost-effectiveness, especially in environments with fluctuating user demands.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing CIAM presents certain challenges. Data migration and integration with legacy systems can be complex. Ensuring user privacy and compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, is paramount. Furthermore, organizations need to address potential security vulnerabilities to maintain user trust. Thorough security audits and rigorous testing throughout the implementation lifecycle are crucial.
Designing a CIAM Solution
A well-structured approach is essential for designing a successful CIAM solution. The initial phase involves defining clear objectives, identifying target users, and mapping out the desired user journeys. Following this, the architecture should be designed with scalability and flexibility in mind, allowing for future growth and adaptation. Careful consideration of security protocols and user privacy safeguards is essential. This stage involves rigorous planning, including the definition of specific use cases and requirements.
Managing User Identities in a CIAM Framework
Various approaches exist for managing user identities within a CIAM framework. Single sign-on (SSO) solutions allow users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials, enhancing convenience and streamlining the user experience. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring multiple verification steps, safeguarding sensitive information. Federated identity solutions enable seamless authentication across different organizations and platforms, fostering collaborative environments. Implementing a robust identity governance and administration (IGA) framework is essential to manage user accounts and access rights effectively.
Use Cases Across Industries
| Industry | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Financial Services | Secure online banking, account management, personalized financial advice |
| Retail | Personalized shopping experiences, targeted promotions, loyalty programs |
| E-commerce | Secure online transactions, personalized recommendations, improved customer support |
| Healthcare | Secure patient portals, streamlined appointment scheduling, and improved communication.n |
| Education | Secure student portals, online learning platforms, personalized learning experiences |
Security Considerations and Best Practices
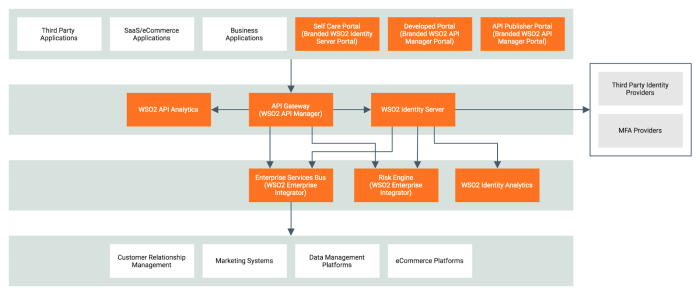
Source: thenewstack.io
CIAM architectures, while offering significant benefits, are susceptible to various security vulnerabilities. Robust security measures are crucial to protect user data and maintain the integrity of the system. A comprehensive approach to security encompasses authentication, authorization, data encryption, and access control, all of which must be meticulously designed and implemented.
A robust security strategy for CIAM systems is paramount. Failing to address potential vulnerabilities can lead to data breaches, reputational damage, and significant financial losses for organizations. Thorough security considerations throughout the design and implementation phases are essential for building a trustworthy and reliable CIAM platform.
Security Vulnerabilities in CIAM
CIAM systems, by their very nature, handle sensitive user data. This inherent sensitivity exposes them to several potential vulnerabilities, including, but not limited to, vulnerabilities in authentication mechanisms, weak access controls, and insufficient data encryption. Improperly configured systems can allow unauthorized access to user data, compromise account credentials, and potentially lead to data breaches. Furthermore, inadequate security measures can leave users exposed to phishing attacks or other malicious activities.
Security Measures and Best Practices
Effective security measures are crucial to mitigate the identified vulnerabilities. Implementing strong authentication protocols, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Robust access controls, restricting access to only authorized personnel, are equally important. Implementing strong encryption protocols, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), for sensitive data at rest and in transit is critical to protecting user data confidentiality. Regular security audits and penetration testing are vital to identify and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Authentication and Authorization in CIAM
Authentication verifies the identity of a user, while authorization determines what resources and actions the authenticated user is permitted to access. In a CIAM system, robust authentication mechanisms, such as strong passwords, MFA, and biometrics, are essential to ensure that only legitimate users gain access. Authorization, often based on role-based access control (RBAC), controls the specific actions users can perform within the system. This combination of authentication and authorization creates a secure and controlled environment.
Data Encryption and Access Control
Data encryption plays a pivotal role in protecting sensitive user data. Encrypting data both at rest (stored in databases) and in transit (during transmission) prevents unauthorized access. Access control, typically implemented using RBAC, defines who can access specific data and what actions they can perform on that data. A layered approach, combining encryption and access control, creates a strong defense against data breaches.
Protecting User Data and Privacy
User data privacy is paramount in CIAM. Implementing comprehensive data protection policies and adhering to industry regulations, such as GDPR, is essential. Transparency about data usage practices and obtaining explicit user consent for data collection and processing are vital. Anonymization or pseudonymization techniques can further protect user privacy while still enabling the system to function effectively.
Security Threats and Mitigation Strategies
A well-defined strategy to mitigate potential threats is critical. This table articulates various security threats and their corresponding mitigation strategies:
| Threat | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Unauthorized Access | Strong authentication methods (e.g., MFA), robust access controls (e.g., RBAC), and regular security audits |
| Data Breaches | Data encryption at rest and in transit, secure storage solutions, and incident response planning |
| Phishing Attacks | User awareness training, secure email protocols, and robust spam filters |
| Malware Infections | Regular software updates, anti-malware protection, and secure software development practices |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks | Load balancing, intrusion detection systems, and network security measures |
Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
The customer identity and access management (CIAM) landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing user expectations. This dynamic environment necessitates a forward-thinking approach to CIAM architecture, anticipating and incorporating emerging technologies to maintain a competitive edge. Adapting to these shifts is critical for businesses to retain customer loyalty and satisfaction in a technologically advanced world.
CIAM is not a static system; it’s a living entity that must adapt to the changing technological and user landscape. This involves embracing new technologies, anticipating future trends, and continuously enhancing the CIAM experience to meet the evolving demands of users.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are transforming CIAM by automating tasks, enhancing personalization, and improving security. AI-powered solutions can analyze vast amounts of user data to identify patterns and anomalies, enabling proactive security measures. For example, machine learning algorithms can detect fraudulent login attempts in real time, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Moreover, AI algorithms can be used to predict customer behavior, allowing businesses to tailor their CIAM experiences to specific user needs. This leads to a more seamless and personalized user journey, fostering customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Evolution of Cloud Computing and Microservices
Cloud computing and microservices are fundamentally altering CIAM architectures. Cloud-based CIAM solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to fluctuating demands. Microservices architectures enable modularity and independent deployment of CIAM components, facilitating faster development cycles and more efficient updates. This agility is crucial for responding to evolving market needs and maintaining a competitive advantage. The integration of these technologies streamlines the CIAM process, offering businesses greater control over their customer data and user experience.
Adapting to Evolving User Expectations
User expectations are constantly evolving, demanding seamless and personalized experiences across all touchpoints. CIAM architectures need to address these evolving needs by offering personalized onboarding processes, intuitive user interfaces, and secure access methods. The shift toward mobile-first and omnichannel experiences requires CIAM solutions to be responsive, secure, and user-friendly across various devices and platforms. Businesses need to ensure a unified experience across all touchpoints, whether a user is interacting with the platform via desktop, mobile, or other channels.
Potential Future Advancements
- Enhanced Personalization: AI-driven personalization can tailor the CIAM experience to individual user preferences, making it more engaging and relevant. For instance, personalized recommendations for security settings or account management tools can significantly improve the user experience. This level of customization can increase customer satisfaction and retention.
- Improved User Experience: A more intuitive and user-friendly interface can significantly improve the customer journey. This includes simpler account creation, faster login processes, and streamlined password management. The focus is on frictionless experiences, allowing users to interact with the system efficiently and without difficulty.
- Increased Security Measures: Advancements in biometric authentication, multi-factor authentication, and data encryption can bolster security measures. This will reduce vulnerabilities and protect user data against unauthorized access and cyber threats. Enhanced security is essential for building trust and maintaining customer confidence.
- Integration with Other Systems: The seamless integration of CIAM with other enterprise systems, such as CRM and marketing platforms, can create a more comprehensive customer view and facilitate data-driven decision-making. This integration streamlines the user journey, allowing for a more cohesive and personalized customer experience.
End of Discussion
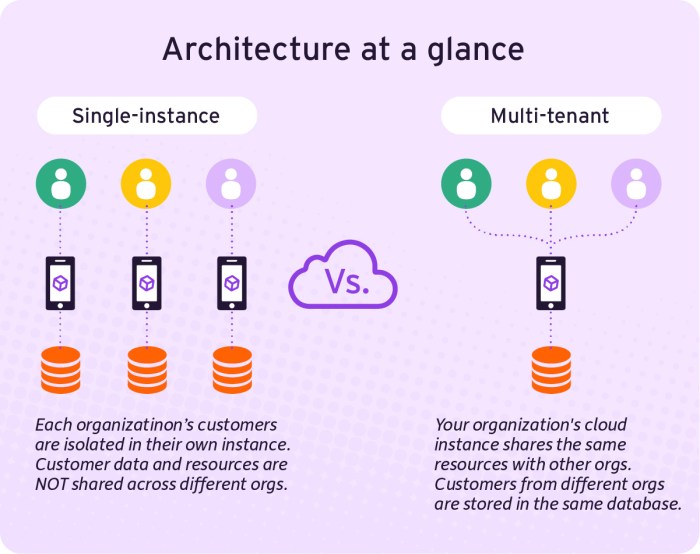
Source: website-files.com
In conclusion, CIAM architecture offers a powerful framework for managing user identities and access securely and efficiently. Its evolution reflects the growing complexity of modern digital interactions and the increasing importance of user-centric design. From the core components to future trends, CIAM’s impact on the digital landscape is undeniable. The benefits of streamlined user experiences, enhanced security, and increased personalization underscore its significance in today’s competitive market.