A Comfort Heating and Cooling Essentials
A comfortable heating and cooling system is crucial for modern living. It goes beyond simply regulating temperature; it significantly impacts our well-being and the sustainability of our homes. From historical advancements in furnace and air conditioning technology to the latest smart home integrations, this exploration delves into the multifaceted world of comfort heating and cooling. We’ll examine various systems, the factors influencing comfort, and the future of this essential technology.
Different types of heating and cooling systems, like furnaces, air conditioners, and heat pumps, each offer varying energy efficiency and cost profiles. This discussion will analyze these differences, presenting a table that compares their performance. Understanding the factors that influence comfort, such as temperature, humidity, and air quality, is key to creating an optimal indoor environment. A further table will illustrate how different temperature ranges affect comfort levels and potential health impacts.
Introduction to Comfort Heating and Cooling
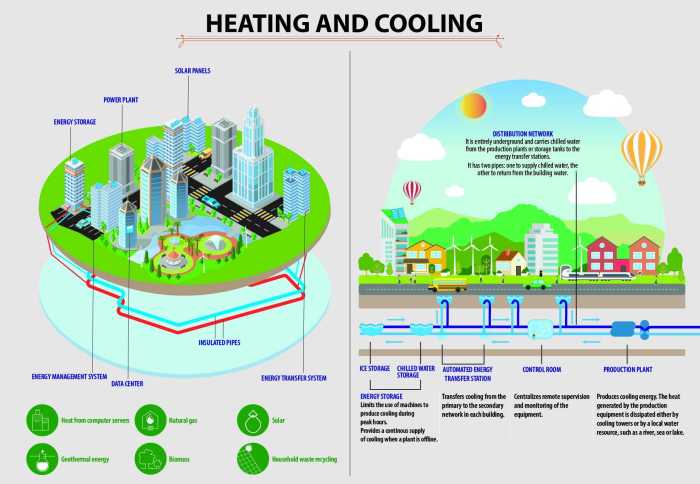
Source: tek-trol.com
Comfort heating and cooling encompass the technologies and systems designed to maintain a comfortable indoor environment. This involves precisely controlling temperature and humidity levels, catering to individual preferences and external weather conditions. The goal is to create a pleasant and healthy indoor atmosphere regardless of the external climate.
Historically, comfort heating and cooling systems have undergone significant advancements. Early methods relied on rudimentary technologies, such as fireplaces and natural ventilation. Over time, innovations in materials, engineering, and energy efficiency have led to the sophisticated systems available today. This evolution reflects a growing societal need for thermal comfort and the continuous pursuit of better solutions.
Types of Heating and Cooling Systems
Various systems are available for achieving comfortable heating and cooling. Each type utilizes different principles and technologies, resulting in varying levels of energy efficiency and cost. The choice of system often depends on factors like building design, climate, and budget.
- Furnaces: Furnaces are common heating systems that use combustion to generate heat. They are typically fueled by natural gas, propane, or oil. Modern furnaces often incorporate advanced features like electronic ignition and automatic safety controls.
- Air Conditioners: Air conditioners use refrigerants to absorb heat from the indoor air and release it outdoors. They effectively lower indoor temperatures and humidity levels, particularly in warm climates. Different types of air conditioners, such as window units, central air conditioners, and portable units, cater to various needs and space requirements.
- Heat Pumps: Heat pumps are versatile systems that can both heat and cool a space. In heating mode, they extract heat from the outside air and transfer it indoors. In cooling mode, they reverse the process, removing heat from the indoor air and releasing it outside. Their energy efficiency is often higher than traditional heating and cooling systems, especially in moderate climates.
Key Factors Influencing System Design
Several key factors significantly impact the design and performance of comfort heating and cooling systems. These factors include the building’s insulation, the climate conditions, and the occupants’ preferences. Optimizing these elements leads to systems that provide comfortable conditions while minimizing energy consumption.
- Building Insulation: Proper insulation significantly affects a system’s performance. High insulation levels reduce heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, thereby minimizing the energy needed to maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
- Climate Conditions: Climate plays a crucial role in selecting the right system. Systems designed for hot and humid climates differ from those suitable for cold and dry climates. Local weather patterns, such as average temperatures and humidity levels, influence the design parameters.
- Occupant Preferences: Occupant comfort is a primary consideration. Systems should be adaptable to individual preferences, enabling adjustments for temperature and humidity levels. Factors like the number of occupants and their activity levels also influence the design.
Energy Efficiency Comparison, A Comfort Heating and cooling
Energy efficiency is a crucial aspect of comfort heating and cooling systems. Systems with higher energy efficiency ratings consume less energy to maintain the desired temperature, translating to lower utility bills and a smaller environmental impact.
| System Type | Energy Efficiency Rating | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| High-Efficiency Furnace (Natural Gas) | AFUE 95% | $5,000 – $8,000 |
| Central Air Conditioner (Variable Speed) | SEER 16 | $4,000 – $7,000 |
| Heat Pump (High Efficiency) | HSPF 12 | $6,000 – $10,000 |
Note: Energy efficiency ratings and costs are examples and may vary based on specific models and installation requirements.
Factors Affecting Comfort
Optimizing comfort in a space hinges on understanding the intricate interplay of various factors. A well-designed heating and cooling system must consider more than just temperature; humidity, air quality, and personalized preferences all play crucial roles in creating a truly comfortable environment. A balanced approach to these elements is vital for occupant well-being and satisfaction.
Impact of Temperature, Humidity, and Air Quality
Temperature, humidity, and air quality are interconnected components of indoor environmental comfort. The perceived comfort of a space is significantly influenced by the interaction of these factors. Maintaining an appropriate temperature range, alongside suitable humidity levels and clean, fresh air, is key to maximizing occupant comfort. Inadequate control of any of these elements can lead to discomfort and potentially health issues. Air quality, in particular, plays a crucial role in overall well-being, impacting respiratory health and general productivity.
Importance of Personalized Comfort Settings
Individual preferences vary significantly regarding temperature, humidity, and air quality. What feels comfortable to one person may be uncomfortable for another. A personalized approach to comfort settings is therefore crucial. By incorporating individual preferences into the heating and cooling system, the occupants can experience greater satisfaction and productivity. Consideration of individual sensitivities and needs, such as those with allergies or respiratory conditions, is also essential for optimal comfort.
Influence on Health and Well-Being
Indoor environmental conditions can significantly influence occupant health and well-being. Factors such as temperature extremes, fluctuating humidity, and poor air quality can trigger or exacerbate various health issues. Properly regulated temperature and humidity levels can reduce the risk of respiratory problems and promote a healthier indoor environment. Moreover, maintaining clean air quality contributes to overall well-being and productivity.
Temperature Range and Comfort
The following table illustrates how different temperature ranges affect comfort levels and potential health impacts. It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and individual responses may vary.
| Temperature Range (°C) | Comfort Level | Potential Health Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| 18-22 | Generally comfortable for many | Potential for mild discomfort in extreme cases, but generally healthy range. |
| Below 18 | Cold, potentially uncomfortable | Increased risk of colds, flu, and other illnesses, particularly for vulnerable populations. Potential for muscle stiffness and discomfort. |
| Above 22 | Warm, potentially uncomfortable for some | Increased risk of heat exhaustion or heatstroke in prolonged exposure. Potential for discomfort and reduced productivity. |
Technologies and Innovations
Modern comfort heating and cooling systems are constantly evolving, incorporating innovative technologies to enhance efficiency, comfort, and user experience. These advancements are driven by the need for greater energy savings and more responsive control over indoor environments. The integration of smart home technologies plays a crucial role in this evolution, offering significant benefits for both homeowners and the environment.
Emerging Technologies
Several emerging technologies are reshaping the landscape of comfort heating and cooling. Smart thermostats, for example, utilize advanced algorithms to learn user preferences and automatically adjust settings for optimal comfort and energy efficiency. Variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems are another important development, allowing for precise temperature control in individual zones within a building, reducing energy waste, and enhancing occupant satisfaction.
Smart Home Integration
Integrating comfort heating and cooling systems with smart home platforms offers significant advantages. Users can control their systems remotely through mobile apps, adjusting temperatures, scheduling operations, and receiving alerts regarding maintenance needs. This remote control empowers users to optimize energy consumption and respond quickly to changes in environmental conditions. Moreover, smart home integration allows for seamless interaction with other home systems, creating a unified and user-friendly environment.
Automation for Energy Efficiency
Automation plays a vital role in optimizing energy efficiency in heating and cooling systems. Smart thermostats, in particular, leverage sophisticated algorithms to analyze historical usage patterns and adjust settings dynamically, leading to significant energy savings. Predictive maintenance capabilities also enable proactive responses to potential issues, preventing costly repairs and ensuring consistent system performance.
Latest Advancements in Comfort Cooling and Heating Technology
A variety of advancements are continually emerging in comfort cooling and heating technology. These include the development of more efficient heat pumps, enhanced insulation materials, and advanced air filtration systems. Furthermore, innovations in refrigerant technology are focusing on environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional refrigerants.
Smart Thermostat Features and Energy Savings
Smart thermostats offer diverse features, each impacting energy savings in different ways. Geofencing, for example, automatically adjusts the temperature based on the user’s location, preventing unnecessary energy use when the home is unoccupied. Learning capabilities allow the thermostat to adapt to user preferences, further optimizing comfort and efficiency. Scheduled adjustments enable users to program the system for specific times and conditions, ensuring desired comfort levels at predetermined moments. The comparison of these features reveals that each contributes to energy savings, with geofencing often yielding the most significant results when applied in conjunction with other smart features.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability

Source: residencestyle.com
Optimizing energy efficiency in heating and cooling systems is crucial for both financial savings and environmental responsibility. Modern homes and businesses can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and lower utility bills by implementing various energy-saving strategies. These advancements not only benefit the individual user but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
Importance of Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency in heating and cooling systems is paramount. Reduced energy consumption directly translates to lower utility bills, benefiting homeowners and businesses financially. Furthermore, minimizing energy use minimizes the environmental impact of these systems, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to a more sustainable future. The adoption of energy-efficient technologies is a key step in mitigating climate change.
Methods for Improving Energy Efficiency
Several strategies can improve the energy efficiency of heating and cooling systems. High-performance insulation materials significantly reduce heat loss or gain, thereby minimizing the energy required to maintain desired temperatures. Smart thermostats, equipped with advanced sensors and control systems, optimize heating and cooling based on occupancy and external conditions, reducing unnecessary energy consumption. Regular maintenance of equipment ensures optimal performance and reduces energy waste. The proper sealing of ducts and windows also contributes to energy efficiency. These measures, when combined, can yield substantial energy savings.
Environmental Impact of Heating and Cooling Solutions
Different heating and cooling solutions have varying environmental impacts. Fossil fuel-based systems, such as traditional furnaces and boilers, contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Conversely, renewable energy sources, such as geothermal and solar systems, produce minimal emissions, making them more environmentally friendly. The choice of heating and cooling system directly influences the carbon footprint of a building or home.
Role of Sustainable Materials
Sustainable materials play a vital role in the construction and appliance components of heating and cooling systems. Using recycled or reclaimed materials in construction minimizes the environmental impact of the system’s manufacturing process. Employing environmentally friendly refrigerants in cooling systems reduces harmful emissions. The selection of sustainable materials is crucial in reducing the overall environmental footprint of the system.
Energy-Efficient Heating and Cooling Solutions
Implementing energy-efficient solutions is crucial for sustainable heating and cooling systems. A comparison of various options illustrates the benefits.
| Solution | Energy Savings (%) | Environmental Impact | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-efficiency heat pumps | 30-50% | Lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional systems | Moderate to high upfront cost but potentially lower long-term operating costs |
| Smart thermostats | 10-20% | Reduces energy waste by optimizing usage based on real-time conditions | Low upfront cost |
| Insulated windows and doors | 10-15% | Reduces heat loss/gain, leading to lower energy consumption | Moderate upfront cost |
| Geothermal heating and cooling | 30-40% | Utilizes naturally occurring underground temperatures for heating and cooling, generating zero emissions | High upfront cost but potentially significant long-term savings |
Future Trends and Projections
The comfort heating and cooling industry is poised for significant transformation in the coming years. Advancements in technology, coupled with growing environmental concerns, will reshape the landscape of indoor climate control. This section explores emerging trends, potential technological leaps, and the evolving role of personalized comfort systems in the future.
Future Trends in Comfort Technology
The future of comfort heating and cooling will be characterized by a shift toward more intelligent, sustainable, and personalized systems. Increased integration with smart home technologies will be commonplace, allowing users to remotely manage their comfort settings and optimize energy consumption. The emphasis will also be on seamless integration with other household appliances and systems, for example, lighting and security.
Advancements in Materials and Technologies
Materials with enhanced thermal properties are likely to become more prevalent in construction and appliance manufacturing. This includes the development of advanced insulation materials, more efficient heat exchangers, and smarter refrigerants with reduced environmental impact. For instance, research into phase-change materials, which can absorb and release heat effectively, is yielding promising results for thermal storage solutions. This translates into more energy-efficient systems and improved comfort levels.
Personalized Comfort Systems
The future will see an increasing emphasis on personalized comfort systems. These systems will leverage data analytics to understand individual preferences and adapt to real-time needs. Smart sensors, connected thermostats, and wearable devices will provide detailed information on user activity and comfort levels, allowing systems to optimize temperature, airflow, and other parameters for each individual or occupant. Examples include personalized temperature settings for individual bedrooms in a house or temperature variations within a large office space.
Impact of Climate Change
Climate change is expected to significantly influence future heating and cooling needs. More frequent and intense extreme weather events, including heat waves and cold snaps, will necessitate the development of more resilient and adaptable systems. The focus will be on systems capable of handling fluctuating temperatures and maintaining consistent comfort levels, even under challenging conditions. This is already visible in the increasing demand for advanced climate control solutions in regions experiencing amplified climate extremes.
A Futuristic Home with Innovative Comfort Systems
Imagine a home equipped with a sophisticated climate control system. The house’s facade incorporates advanced photovoltaic panels that harvest solar energy, reducing reliance on the grid. Interior walls are constructed from self-regulating thermal materials, maintaining a comfortable temperature without significant energy expenditure. Smart thermostats, integrated with wearable devices, adjust the temperature based on real-time activity levels, preferences, and even physiological data, for example, by monitoring heart rate variability. Integrated air filtration systems monitor indoor air quality and adjust the filtration based on occupancy levels and environmental conditions, such as pollen count. This proactive approach to climate control, coupled with smart energy management, minimizes environmental impact while maximizing occupant comfort.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Source: com.au
Regular maintenance is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of heating and cooling systems. Proper upkeep prevents costly repairs and ensures consistent comfort throughout the year. Neglecting maintenance can lead to significant efficiency drops, increased energy bills, and even system failures.
A proactive approach to maintenance, including routine checks and necessary repairs, translates to a healthier indoor environment and a more sustainable approach to home comfort. This proactive approach also significantly reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and the associated inconvenience and expense.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance schedules are vital for the continued operation of comfort systems. They include inspections, cleaning, and adjustments to ensure the system runs efficiently. Proper maintenance not only enhances comfort but also significantly extends the lifespan of the equipment. A well-maintained system operates at peak efficiency, using less energy and reducing operating costs. It also helps prevent potential issues that might arise from wear and tear or neglect, such as refrigerant leaks or motor malfunctions.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Steps
Troubleshooting common issues in heating and cooling systems involves identifying the root cause. By systematically checking various components and using appropriate diagnostic tools, one can determine the nature of the problem. This approach is essential for efficient repairs and timely solutions.
Troubleshooting Table
| Issue | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| System not turning on | Faulty power supply, tripped circuit breaker, or a blown fuse. | Check the power supply, verify the circuit breaker, and replace the fuse if necessary. Ensure proper electrical connections. |
| Inadequate heating or cooling | Dirty air filters, restricted airflow, low refrigerant levels, or a malfunctioning thermostat. | Clean or replace air filters, check for obstructions in the vents, ensure proper refrigerant levels, and calibrate the thermostat. |
| Unusual noises | Loose components, worn-out parts, or obstructions in the system. | Identify the source of the noise. Check for loose parts, replace worn components if needed, and ensure there are no obstructions in the ductwork. |
| High energy bills | Poor insulation, inadequate sealing, or malfunctioning components. | Inspect insulation around the ductwork and the home. Check for air leaks around windows and doors. Verify the efficiency of components and consider upgrading to more energy-efficient models. |
| Water leaks | Damaged condensate drain line, malfunctioning water pump, or a leak in the cooling coils. | Check the condensate drain line for clogs or leaks. Inspect the water pump and the cooling coils. If needed, replace the affected parts. |
Optimizing System Performance
Optimizing heating and cooling system performance involves several key steps. Ensuring proper airflow, cleaning air filters regularly, and adjusting the thermostat settings according to needs are critical steps. These actions not only enhance comfort but also contribute to energy savings.
Role of Professional Maintenance
Professional maintenance plays a vital role in extending the lifespan of heating and cooling systems. Certified technicians possess the expertise and tools to diagnose complex issues and provide necessary repairs. This expert knowledge ensures that the systems function optimally, reducing the risk of future problems and maximizing their operational efficiency.
Closure: A Comfort Heating And Cooling
In conclusion, achieving comfort in heating and cooling is a complex interplay of technology, design, and sustainability. We’ve explored the evolution of these systems, from basic designs to advanced smart home integrations, highlighting their crucial role in our daily lives. Furthermore, the importance of energy efficiency and sustainable practices cannot be overstated, as they significantly impact our environment and our financial well-being. The future of comfort heating and cooling promises even greater innovation, with personalized systems and advanced technologies set to shape the indoor environments of tomorrow.