Comfort Service Heating and Air A Comprehensive Guide
Comfort service heating and air conditioning are a vital aspect of modern living, encompassing a wide range of services that ensure thermal comfort and well-being. This guide delves into the intricacies of this sector, exploring the diverse types of services offered, from installation and maintenance to emergency repairs.
The discussion will cover customer needs and preferences, examining how factors like climate, lifestyle, and budget influence choices. Different service delivery processes will be analyzed, along with an exploration of technological advancements that are transforming the industry. Finally, we’ll touch upon market trends, environmental considerations, safety protocols, and the importance of maintaining strong customer relationships in this crucial sector.
Defining Comfort Service Heating and Air
Comfort service heating and air conditioning encompasses a broad range of services designed to maintain a comfortable indoor environment. This goes beyond simply providing heat or cool air; it involves understanding customer needs and preferences to optimize thermal comfort, indoor air quality, and overall satisfaction. A comprehensive comfort service provider anticipates and addresses various needs, from routine maintenance to emergency repairs.
Defining Heating, Air Conditioning, and Comfort Service
Heating, air conditioning, and comfort service are interconnected but distinct concepts. Heating systems provide warmth, while air conditioning systems regulate temperature and humidity. Comfort service, however, integrates these functions with a focus on customer satisfaction. It’s not merely about providing heat or cool air; it’s about creating a consistently comfortable and healthy indoor environment. A comfort service provider considers factors like temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, air quality, and even personal preferences when addressing customer needs. The difference lies in the holistic approach that comfort service takes, moving beyond basic functionality to provide a superior experience.
Scope of Services
Comfort Service Heating and Air encompasses a wide range of services, including installation, maintenance, repair, and emergency services. Installation involves setting up new systems, ensuring proper functionality, and adherence to safety regulations. Maintenance encompasses regular inspections, cleaning, and adjustments to prevent potential issues and prolong system lifespan. Repair services address malfunctions and breakdowns, restoring the system to optimal operation. Emergency services are crucial for addressing critical issues, such as sudden system failures during extreme weather conditions, ensuring rapid response and restoration of comfort.
Types of Heating and Cooling Systems
Understanding the various types of heating and cooling systems is crucial for effective comfort service. Different systems offer varying levels of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact.
| System Type | Description | Pros | Cons | Comfort Service Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furnaces (Gas, Oil, Electric) | Burn fuel to heat air circulated through ducts. | Relatively affordable initial cost, widespread availability. | It can be less energy-efficient, have potential for carbon monoxide leaks, and require regular maintenance. | Regular maintenance is critical for safety and efficiency. Proper venting is essential. |
| Heat Pumps | Use refrigerant to move heat between indoor and outdoor air. | Highly energy-efficient, can provide both heating and cooling, often cost-effective in the long run. | Performance can be affected by extreme temperatures, higher initial cost compared to furnaces. | Proper sizing and installation are critical for optimal performance. Maintenance schedules should be followed. |
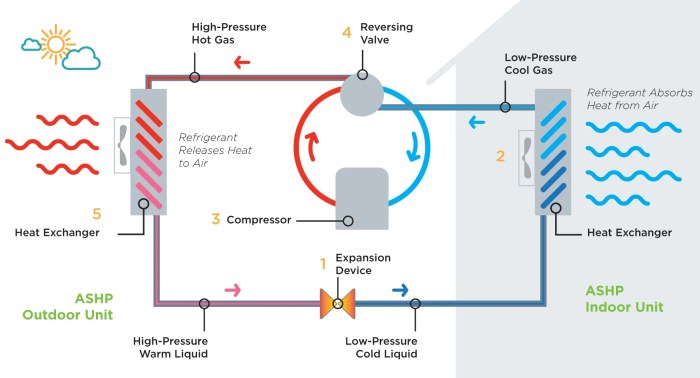
| Air Source Heat Pumps | Use outdoor air to provide heating and cooling. | Highly energy-efficient, environmentally friendly. | Performance is dependent on outdoor temperature, potentially less effective in extremely cold climates. | Careful selection based on local climate conditions is important. |
| Central Air Conditioning Systems | Cool air through refrigerant cycles. | Effective cooling, often reliable and efficient. | It can be expensive to install and maintain, with potential for energy consumption. | Regular maintenance and proper filter replacement are essential. |
| Mini-Split Systems | Use individual units to cool or heat specific areas. | Efficient and quiet operation, flexibility in placement. | Installation can be more complex than other systems, potential cost for larger systems. | Careful consideration of space requirements and zoning needs. |
Customer Needs and Preferences
Understanding customer needs is paramount for a successful comfort service business. Meeting these needs requires a deep understanding of the factors that shape customer preferences, ranging from climate and lifestyle to budget constraints. This knowledge allows for personalized service that addresses individual requirements and ensures customer satisfaction.
Customer comfort is intricately linked to their circumstances and preferences. These factors often dictate the type of heating and cooling systems they desire and the level of service they expect. This section explores the various influences on customer preferences and how personalized service can elevate the customer experience.
Factors Influencing Customer Preferences
Customer preferences for heating and air conditioning services are influenced by several key factors. Climate plays a significant role, with regions experiencing extreme temperatures demanding different solutions. Lifestyle choices, such as the number of occupants in a home or the frequency of use, also influence the type and size of the system required. Budgetary constraints likewise affect the options available, forcing a prioritization of cost-effective solutions.
Customer Segments and Needs
Different customer segments have varying needs when it comes to comfort services. For instance, a family with young children may prioritize energy efficiency and safety features, as well as ease of maintenance. Conversely, a single professional might prioritize aesthetics and energy savings, as well as the convenience of smart home integration. Older adults often need systems that are easy to operate and maintain, with a focus on safety and reliability. Further, businesses might prioritize reliable systems with high capacity to support their daily operations.
Importance of Personalized Service
Personalization is crucial in meeting customer needs effectively. By understanding the unique requirements of each customer, comfort service providers can offer tailored solutions. This might involve recommending specific system types, suggesting maintenance schedules, or providing personalized service plans. A proactive approach, such as regularly checking in with customers and offering preventive maintenance, can foster strong customer relationships and loyalty.
Comparison of Heating and Cooling Systems
| System Type | Energy Efficiency | Cost | Aesthetics | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central Air Conditioning | Generally high, depending on model | Moderate to high upfront cost but potentially lower long-term operational costs | Often integrated into existing systems, potentially less visible | Requires professional maintenance and repair |
| Heat Pumps | Highly efficient, especially in moderate climates | Moderate upfront cost, often with lower operational costs | Can be integrated into existing systems, but aesthetic options vary | Requires professional maintenance and repair |
| Mini-Split Systems | High efficiency, often with variable speed compressors | Moderate to high upfront cost but potentially lower operational costs | Aesthetically flexible, allowing for installation in multiple locations | Requires professional maintenance and repair; potential for DIY maintenance |
| Electric Resistance Heating | Generally lower efficiency | Lower upfront cost but potentially higher operational costs | Often integrated into existing systems, potentially less visible | Requires regular maintenance and repair |
The table above provides a basic comparison of different heating and cooling systems. Specific figures and details will vary based on the specific models, installation, and local energy costs. It is crucial to consult with qualified professionals for detailed analysis and recommendations.
Service Delivery and Processes
A robust service delivery process is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and building a strong reputation in the HVAC industry. A well-defined process ensures consistent service quality, efficient technician deployment, and timely resolution of customer issues. This section details the typical service delivery process for Comfort Service Heating and Air from initial contact to completion.
Our service delivery process prioritizes customer needs and preferences, ensuring a smooth and positive experience. This includes clear communication, prompt response times, and expert technician service.
Typical Service Call Process
The typical service call process involves several key steps, starting with the initial customer contact and concluding with a final follow-up. Understanding each step is vital for maintaining efficiency and exceeding customer expectations.
- Initial Contact and Assessment: Customer inquiries are received via phone, email, or online portal. A dedicated representative assesses the nature of the issue, gathers necessary information (e.g., system type, symptoms, location), and prioritizes the call based on urgency.
- Scheduling Appointments: Based on the assessment and availability, a convenient appointment time is scheduled with the customer. Clear communication about the appointment details, including technician name and expected arrival time, is provided.
- Technician Dispatch and Arrival: Once the appointment is scheduled, the technician is dispatched to the customer’s location. Real-time tracking and updates are provided to the customer regarding the technician’s arrival.
- Service Performance: The technician performs a thorough inspection of the system, diagnoses the issue, and implements the necessary repairs or maintenance. Throughout the process, the technician communicates clearly with the customer about the findings and proposed solutions.
- Completion and Follow-up: Upon completion of the service, the technician confirms the resolution with the customer, ensures the customer is satisfied, and provides any necessary instructions for ongoing system maintenance. A follow-up call is scheduled to ensure the system is functioning properly and address any lingering concerns.
Scheduling Appointments
Efficient scheduling is critical for optimal service delivery. A well-structured system ensures timely responses and minimizes customer wait times.
- Appointment Scheduling System: We utilize a sophisticated scheduling system that integrates with our dispatch software. This system allows for real-time updates, efficient scheduling, and optimized technician routing.
- Customer Communication: Confirmation emails or texts are sent to the customer regarding the appointment details, including technician information and arrival time. We offer multiple communication channels to ensure the customer receives the necessary information.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: We strive to offer flexible appointment times to accommodate customer schedules. If unforeseen circumstances arise, we proactively communicate alternative options with the customer.
Emergency Service
Handling emergencies promptly and efficiently is paramount. A dedicated emergency line and expedited dispatch procedures are in place to address critical situations.
- Emergency Line Access: A dedicated emergency line provides immediate access to our service representatives, who are trained to handle urgent situations and ensure a quick response.
- Priority Dispatch: Emergency calls are prioritized and dispatched immediately to ensure swift technician arrival. This prioritization system guarantees that critical issues receive the attention they require.
- 24/7 Availability: We maintain 24/7 availability for emergency service calls, ensuring prompt response to critical HVAC issues regardless of the time of day.
Customer Service Process
A comprehensive customer service process is critical for managing inquiries, scheduling, and resolving issues.
| Step | Communication Channel | Response Time | Resolution Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Inquiry | Phone, Email, Online Portal | Within 1 hour (priority calls), 24 hours (standard calls) | Escalate to a senior technician or supervisor if necessary |
| Appointment Scheduling | Phone, Email, Online Portal | Within 24 hours | Confirmation via email/text, appointment confirmation |
| Technician Dispatch | Internal Communication System | Immediate dispatch | Technician tracking, real-time updates to customer |
| Service Completion | Phone, Email, In-Person | Within 24 hours (follow-up) | Resolution confirmation, customer feedback collection |
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have profoundly impacted the heating and air conditioning industry, driving efficiency, comfort, and enhanced customer experiences. These innovations are continuously reshaping the landscape of comfort service, providing homeowners and businesses with smarter, more responsive, and environmentally conscious options.
Recent breakthroughs in technology are transforming how heating and air conditioning systems operate and interact with the environment. This evolution extends beyond mere functionality, impacting the overall customer experience through intuitive control and seamless integration with other smart home systems.
Smart Technologies in Optimizing Comfort Service
Smart technologies are revolutionizing comfort services by enabling sophisticated control and monitoring of heating and air conditioning systems. This leads to optimized energy consumption, improved indoor air quality, and increased user convenience. Real-time adjustments based on occupancy and environmental factors enhance comfort and reduce energy waste.
Integration of Digital Platforms in Managing Service Requests and Customer Interactions
Digital platforms have become integral to the management of service requests and customer interactions. This integration streamlines communication, reduces response times, and improves overall customer satisfaction. Online portals and mobile applications facilitate scheduling, tracking service requests, and providing real-time updates. These platforms offer customers increased transparency and control over their service experience.
Comparison of Smart Home Technologies for Heating and Cooling
Various smart home technologies are emerging, each offering unique features and capabilities for managing heating and cooling. These systems range from simple thermostat controls to sophisticated whole-home automation platforms.
- Smart thermostats leverage algorithms and real-time data to optimize temperature settings based on occupancy, weather conditions, and user preferences. They often integrate with voice assistants for hands-free control, further enhancing convenience. Examples include systems from Nest, Ecobee, and Honeywell, demonstrating the widespread adoption of this technology.
- Whole-home automation systems offer a more comprehensive approach to smart home management, encompassing not only heating and cooling but also lighting, security, and entertainment. These systems allow for centralized control and scheduling, providing greater control over the entire home environment. Examples of these systems include systems from Control4 and Lutron, providing sophisticated integration.
- Geothermal systems offer a sustainable alternative for heating and cooling, using the earth’s consistent temperature for heating and cooling. These systems are highly efficient, reducing energy consumption and environmental impact. The initial investment can be higher, but long-term savings and environmental benefits make it an increasingly popular option.
Impact of Smart Technologies on Comfort Service
Smart technologies fundamentally reshape the comfort service experience by automating and optimizing heating and cooling processes. This leads to a more personalized and user-friendly approach, enabling greater control and awareness of energy consumption. The integration of these technologies can also improve indoor air quality and safety by detecting and responding to issues proactively.
Market Trends and Future Projections

Source: highlandac.com
The comfort service heating and air conditioning industry is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses to adapt and thrive in the future market landscape. This section explores current and projected trends, providing insights into the factors influencing the industry’s growth and evolution.
Current Market Trends
The market is currently characterized by a strong emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability. Consumers are increasingly seeking systems that minimize environmental impact while maintaining comfort. This is reflected in the growing popularity of heat pumps, which can serve both heating and cooling functions, and advanced insulation technologies that reduce energy consumption. Smart home integration is another significant trend, enabling remote control and automation of heating and cooling systems, often integrated with other smart home devices.
Emerging Technologies
Several emerging technologies are poised to transform the comfort service industry. These include the development of more efficient and durable heat pump technologies, particularly those utilizing innovative refrigerants. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is also a crucial element, allowing for predictive maintenance and optimized system performance. The use of advanced sensors and data analytics is enabling precise temperature control and energy optimization, often through the implementation of smart thermostats.
Changing Customer Preferences
Customer preferences are shifting towards personalized comfort solutions. Consumers are demanding systems that adapt to their individual needs and preferences, such as adjustable temperature zones within a home. This trend is driving the adoption of smart thermostats and personalized control systems that allow for remote adjustments and schedule optimization based on occupancy and activity. The desire for aesthetically pleasing and integrated designs is also growing, influencing the integration of systems into the overall home design.
Evolving Regulations
Government regulations are playing an increasingly important role in shaping the comfort service industry. Stricter energy efficiency standards are pushing manufacturers to develop more sustainable and efficient systems. These regulations also affect the use of refrigerants, driving the adoption of environmentally friendly alternatives. These evolving regulations are pushing the industry toward more sustainable practices.
Potential Future Trends
The future of the comfort service industry is likely to be defined by further advancements in smart technology, the expansion of renewable energy sources for heating and cooling, and a growing emphasis on personalized comfort experiences. As energy costs continue to fluctuate, consumers will seek out cost-effective and sustainable solutions. The development of systems capable of adapting to changing weather patterns and providing proactive solutions to potential issues is also a strong possibility.
Factors Influencing Market Growth
Several factors are influencing the growth and evolution of the comfort service heating and air conditioning market. Increasing urbanization and population growth contribute to a rising demand for comfort solutions. The rising cost of energy is motivating consumers to seek energy-efficient systems. Technological advancements and the growing popularity of smart home integration are also key drivers. Government incentives and regulations related to energy efficiency further propel the industry’s evolution.
Projected Growth Rates and Market Share
| Heating and Cooling System Type | Projected Growth Rate (5-10 years) | Estimated Market Share (5-10 years) |
|---|---|---|
| High-efficiency heat pumps | 15-20% | 30-40% |
| Smart home integrated systems | 10-15% | 20-30% |
| Geothermal systems | 8-12% | 10-15% |
| Hybrid systems (e.g., heat pump and solar) | 5-10% | 5-10% |
| Traditional HVAC systems (with upgrades) | 2-5% | 20-30% |
Note: Projected growth rates and market share are estimations and may vary based on various economic and environmental factors.
Maintaining Customer Relationships
Cultivating strong customer relationships is paramount in the comfort service industry. Repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals are directly linked to the quality of the customer experience. Building trust and fostering loyalty requires consistent effort and a genuine commitment to customer satisfaction.
Effective customer relationship management (CRM) strategies are not just about acquiring new customers; they are about retaining existing ones and encouraging their continued patronage. Proactive communication, responsiveness to needs, and a personalized approach are key components of successful CRM programs.
Importance of Strong Customer Relationships
Maintaining strong customer relationships is crucial for long-term success in the comfort service industry. Loyal customers are more likely to recommend services to friends and family, generating valuable referrals. They also tend to be more forgiving of occasional issues and more receptive to new offerings. This fosters a positive feedback loop, contributing significantly to business growth and sustainability.
Successful Customer Relationship Management Strategies
Several strategies contribute to successful CRM in the comfort service industry. Proactive communication, such as regular follow-up calls or emails after service, can strengthen customer relationships. Personalized service, tailored to individual customer needs and preferences, is another important element. Offering exclusive discounts or promotions to loyal customers further reinforces the value of their patronage.
Effective Communication Throughout the Service Process
Clear and consistent communication is vital throughout the service process. This includes providing customers with accurate timelines for service completion, promptly addressing any concerns, and actively listening to their feedback. Maintaining open communication channels, such as dedicated email addresses or phone lines, facilitates smooth interaction.
Exceptional Customer Service and Repeat Business
Exceptional customer service is not just a desirable trait; it is a fundamental component of long-term success. Positive experiences lead to customer loyalty, encouraging repeat business and referrals. Companies that prioritize customer satisfaction tend to experience higher retention rates and increased profitability. Addressing customer issues promptly and resolving complaints effectively demonstrates a commitment to their well-being, which is crucial in building lasting relationships.
Examples of Successful CRM Practices
Numerous examples illustrate successful CRM practices. Companies that provide detailed service reports after each visit, offering transparent pricing and service options, often see high customer satisfaction. Providing a dedicated customer service representative who is readily available to answer questions and address concerns demonstrates a commitment to excellent service. This level of responsiveness and proactiveness builds trust and encourages repeat business. In some cases, companies have implemented loyalty programs rewarding frequent customers with discounts or exclusive perks.
Environmental Considerations: Comfort Service Heating And Air
The comfort service industry plays a significant role in a building’s energy consumption, directly impacting the environment. Choosing sustainable practices and technologies is crucial to minimizing this impact and contributing to a healthier planet. This section explores the environmental footprint of various heating and cooling systems, highlighting environmentally friendly options and the importance of energy efficiency.
The environmental impact of heating and cooling systems extends beyond the direct energy consumption. Manufacturing processes for equipment and disposal of outdated systems contribute to overall environmental stress. Careful consideration of the entire lifecycle of these systems is necessary for a holistic approach to sustainability.
Environmental Impact of Different Heating and Cooling Systems, Comfort service heating and air
Various heating and cooling systems have different environmental footprints. The selection of a system should consider factors like energy source, efficiency ratings, and potential for greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing energy-efficient systems reduces the overall environmental burden.
| Heating/Cooling System | Environmental Impact (General Overview) |
|---|---|
| Fossil Fuel-based Systems (e.g., furnaces, boilers) | High carbon emissions during operation, potential for air and water pollution. Manufacturing processes can also have a significant environmental impact. |
| Electric Systems (e.g., heat pumps, electric resistance heating) | Lower carbon emissions than fossil fuel-based systems, but emissions depend on the source of electricity generation. Manufacturing and disposal processes also have environmental implications. |
| Renewable Energy Systems (e.g., geothermal, solar thermal) | Lower carbon emissions during operation generally have a smaller environmental footprint throughout their lifecycle, depending on the specific technology and installation process. |
Environmentally Friendly Technologies and Practices
Implementing environmentally friendly technologies and practices in the comfort service industry is essential. This involves choosing energy-efficient equipment, optimizing system operation, and utilizing renewable energy sources. Examples include high-efficiency heat pumps, smart thermostats, and solar thermal panels.
- High-Efficiency Heat Pumps: These systems can provide heating and cooling more efficiently than traditional systems, reducing energy consumption and lowering carbon emissions.
- Smart Thermostats: These devices allow for precise temperature control, reducing energy waste by optimizing heating and cooling cycles based on occupancy and weather patterns. This can significantly reduce energy use, leading to lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Solar Thermal Panels: These panels collect solar energy to heat water or provide supplemental heating, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. In many regions, solar thermal systems are becoming more economically viable, further incentivizing their adoption.
Importance of Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Energy efficiency and sustainability are paramount in the comfort service industry. Implementing energy-efficient solutions reduces energy consumption, lowers operating costs, and minimizes the environmental impact of heating and cooling systems. Sustainable practices also ensure long-term viability and contribute to a more environmentally conscious approach.
“Energy efficiency is not just about saving money; it’s about building a more sustainable future.”
Safety and Compliance

Source: minutemanheatingandac.com
Ensuring the safety of both technicians and customers is paramount in the comfort service industry. Proper safety procedures, adherence to regulations, and meticulous maintenance practices are crucial for preventing accidents, injuries, and property damage. This section articulates the importance of safety protocols and details relevant regulations.
Importance of Safety Procedures
Safety procedures are fundamental to minimizing risks associated with heating and air conditioning systems. They protect technicians from potential hazards like electrical shocks, falls, and exposure to harmful substances. Furthermore, they safeguard customers by preventing equipment malfunctions that could cause property damage or personal injury. Adhering to safety procedures fosters a trustworthy and responsible work environment for all parties involved.
Safety Precautions and Best Practices
A proactive approach to safety is essential. These best practices contribute to a safer work environment for technicians and minimize risks for customers.
- Regular equipment inspections are critical to identifying potential hazards early on.
- The proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, gloves, and appropriate footwear, is mandatory.
- Maintaining a clean and organized workspace prevents accidents caused by clutter or obstructions.
- Strict adherence to the manufacturer’s instructions for equipment operation, maintenance, and repair is vital.
- Proper lockout/tagout procedures must be followed during any maintenance or repair work.
Regulations and Standards
Compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards is a legal requirement and crucial for maintaining the safety of heating and cooling systems.
- National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines must be followed for all electrical work associated with HVAC systems.
- Local building codes often dictate specific requirements for installation and maintenance, which vary by region.
- Standards set by organizations like ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers) provide essential guidelines for the safe design, operation, and maintenance of HVAC systems.
- Safety certifications and licenses for technicians are necessary to ensure that qualified personnel perform installations, repairs, and maintenance.
Safety Protocols for Service Visits
A clear protocol for technicians and customers ensures a safe and efficient service experience.
| Category | Technician Protocols | Customer Protocols |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Visit | Confirm appointment details, gather necessary information, and prepare required tools and equipment. Check for potential hazards in the customer’s home. | Ensure technician access to the equipment, have relevant paperwork prepared, and communicate any known issues. |
| During Visit | Follow established safety procedures, wear appropriate PPE, and report any safety concerns immediately. Isolate potential hazards, such as downed power lines. | Remain at a safe distance from the technician and equipment; do not attempt to assist during the service. |
| Post-Visit | Ensure all tools and equipment are properly stored and the work area is clean. Provide the customer with a detailed report of the service performed. | Confirm understanding of the work performed and follow any recommendations. |
Final Wrap-Up

Source: americancoolingandheating.com
In conclusion, comfort service heating and air conditioning represents a dynamic industry adapting to evolving customer needs and technological advancements. From understanding customer preferences to implementing sustainable practices and ensuring safety, this guide highlights the multifaceted nature of this essential service. The future of comfort service heating and air promises exciting developments driven by innovation and a commitment to customer satisfaction.